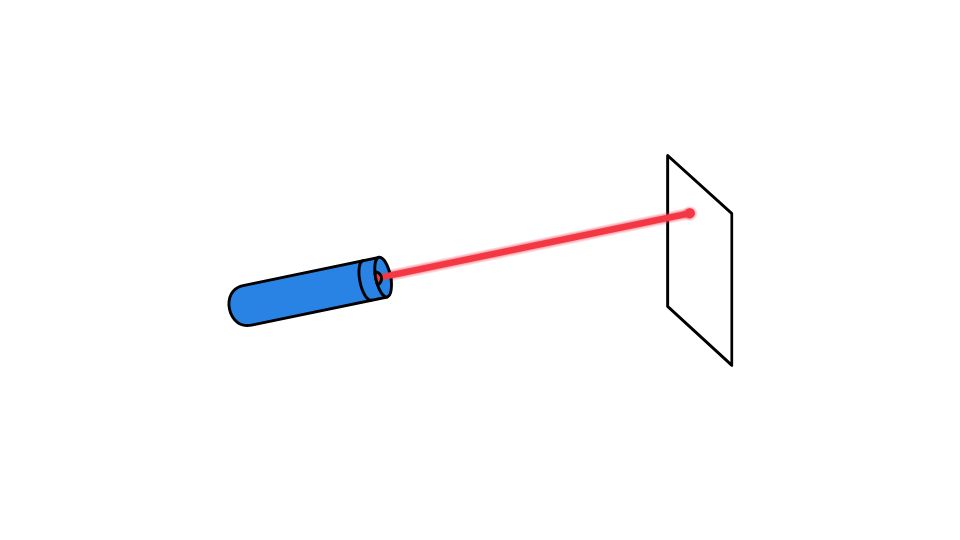
Ever wondered how those tiny laser pointers create such a powerful beam? You know, the ones people use to torment cats or make their PowerPoint presentations more exciting?
These pocket-sized light sabers work through some seriously cool physics that transforms ordinary electricity into a focused beam that can travel incredible distances without spreading out much.
Let’s break down the magic behind these handy devices – from the tiny components inside to why green lasers look cooler than red ones when you point them at the night sky.

How Laser Pointers Actually Work
Unlike your average lightbulb that spews light in all directions, a laser pointer creates a tight, organized beam where all the light waves march in perfect formation. This is why that tiny dot can appear on a wall hundreds of feet away instead of fading out like a flashlight beam.
The word “laser” itself is actually an acronym that stands for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.” Fancy, right? But don’t worry – I’ll explain it in normal human language.
The Core Components

When you click that button on your laser pointer, here’s what happens:
Batteries provide power to the internal circuit – nothing magical here, just your standard electrical energy.
The laser diode (a specialized semiconductor) takes that electricity and converts it into light. This tiny component is the heart of your laser pointer and determines what color light it produces.
Mirrors inside the diode bounce the light back and forth, amplifying it in the process.
A lens at the tip focuses this light into the beam that projects outward.
The Physics Behind the Beam
What makes laser light different from regular light is three key properties:
1. It’s Monochromatic
Your standard light bulb produces a rainbow of different wavelengths. A laser, however, produces light of just one specific wavelength (color). Red lasers typically emit light at around 650 nanometers, while green ones shine at about 532 nanometers.
2. It’s Coherent
In a laser pointer, all the light waves are perfectly in sync with each other – they rise and fall together. This is like having thousands of people jumping rope in perfect harmony, rather than each person jumping whenever they feel like it. This coherence is why laser light is so intense and can travel so far.
3. It’s Highly Directional
Regular light sources scatter light in all directions. Laser light travels in one narrow, focused beam that spreads very little over distance. This is why you can point that tiny dot at stars that are millions of miles away!
Red vs. Green vs. Blue: What’s the Difference?
Ever notice how green laser pointers seem way cooler than red ones? There’s science behind that!
Red lasers are the simplest and cheapest. They use a single laser diode that directly emits red light.
Green lasers are more complex and actually start with infrared light that gets converted to green through a process called frequency doubling. They appear much brighter to our eyes because human vision is most sensitive to green wavelengths. This is why you can actually see the beam itself in the air on a dusty night!
Blue lasers are the newest kids on the block, using specialized materials to produce their vibrant color.
How Powerful Are They Really?

Most consumer laser pointers are rated at less than 5 milliwatts (mW) of power. That doesn’t sound like much, but it’s all about focus. That tiny amount of energy is concentrated into such a small point that it can actually be dangerous if pointed at someone’s eyes.
In fact, higher-powered lasers (above 5mW) are regulated in many countries because they can cause eye damage faster than you can blink. Those super bright green lasers that can point at stars? Many of them are technically above the legal limit in places like the US.
Everyday Applications Beyond Annoying Your Cat

Laser pointers aren’t just for presentations and tormenting pets. The same technology is used in:
- Barcode scanners at grocery stores
- Laser measuring tools for construction
- Medical devices for precision surgeries
- Astronomical research for measuring distances
The humble laser pointer is actually part of a family of technologies that have revolutionized our world – from DVD players to fiber optic communications that power the internet.
So next time you’re clicking that button to highlight something on your slide deck, take a moment to appreciate the incredible physics happening in the palm of your hand. That tiny beam represents decades of scientific advances packed into a device smaller than your finger.
And maybe, just maybe, resist the urge to shine it in your friend’s eyes. Those concentrated light photons aren’t playing around!